


TapeBlock Teacher Resources
TapeBlocks– Australian Curriculum Connections for Teachers
TapeBlocks provide an opportunity for students to explore knowledge, understanding and skills from multiple dimensions of the curriculum. This includes the learning areas of science and technologies, the critical and creative thinking general capability and the cross-curriculum priority of sustainability.
In the Australian Curriculum V 9.0 Science, students:
- develop Science understanding of forces and motion, and matter and energy (physical sciences)
- learn about science as a human endeavour. Science, technology, and engineering are interconnected; advances in one field can lead to advances in others.
- appreciate the important role of questions, predictions, and hypotheses as critical and creative drivers of scientific inquiry.
In Technologies: Design and Technologies students:
- develop confidence as critical users of technologies and designers and producers of designed solutions.
- investigate, generate, iterate, and analyse ethical and innovative designed solutions for sustainable futures.
- produce design solutions suitable for a range of technologies contexts by selecting and manipulating a range of tools, equipment, materials, systems, and components creatively, competently, and safely; and managing processes.
- evaluate processes and designed solutions and transfer knowledge and skills to new situations.
In Technologies: Digital Technologies students:
- design, create, manage, and evaluate sustainable and innovative digital solutions to meet and redefine current and future needs.
- use computational thinking (abstraction; data collection, representation, and interpretation; specification; algorithms; and implementation) to create digital solutions.
In the Critical and Creative Thinking capability students develop the ability to analyse and inquire by interpreting concepts and problems, drawing conclusions and providing reasons for their decisions.
In the Sustainability cross-curriculum priority students consider design (one of the organising ideas).
- The role of innovation and creativity in sustainably designed solutions, including products, environments, and services.
TapeBlocks provide an opportunity for students to explore materials properties and experiments required to create solutions with them, the type of designed solutions students can make from them, and concepts related to curriculum content in the following ways:
Science – conductive materials, circuits and switches, testing, evaluation, and experimentation
Technologies (creating designed solutions)
- Design and Technologies context: Engineering systems and principles; Materials and Technologies specialisations.
- Digital Technologies: Digital Systems, data representation, implementation (includes programming)
Circuit Safety
There are small parts in the kit so you need to be careful to keep them together so that no younger children swallow them or poke themselves.
You also need to be careful when cutting the tape and pressing components in because some are sharp.
This is electronics but it is very low power. It is different to the power in your home so you cannot play with home electricity.
Lesson Plans
The following section has a range of lessons for use in the classroom. Before undertaking any of the lessons please view the Conductive Tape Tips page to understand the strengths and limitations of conductive tape and make it easier to use and manage
Introduction to TapeBlocks and Circuits
Lesson 1: Introduction to TapeBlock Circuits
Australian Curriculum Link:
- Technologies - Design and Technologies (ACTDEK001)
Hook: Show a short video of creative TapeBlock projects or show several examples of TapeBlocks including power, light, vibration, fan, character, and train
Task: Explore different types of TapeBlocks and their uses.
Learning Outcome: Students will understand the basic concept of TapeBlocks and their potential uses.
Essential Terms: TapeBlocks, building, creativity, circuits, conductive
Inquiry: Where is electricity used. How and why is it different to TapeBlock circuits.
Link: Play with TapeBlocks
Lesson 2: Introduction to Circuits with Pre-made TapeBlocks
Australian Curriculum Link:
- Science - Physical Sciences (ACSSU097)
Hook: Show a simple circuit lighting up an LED.
Task: Create a simple circuit using Pre-made TapeBlocks.
Learning Outcome: Students will learn the basics of electrical circuits.
Essential Terms: Circuit, power, LED, vibration, fan, conductive
Inquiry: How many TapeBlocks can be stacked and still work?
Link: Introduction to TapeBlocks
Introduction to Circuits and Components
Lesson 3: Build a Light Circuits
Australian Curriculum Link:
- Science: Physical Sciences (ACSSU097)
- Technology: Investigating digital systems (ACTDIK007)
Hook: Pass around a light and power TapeBlock for student to activate and discuss where the power flows
Task: Students will create a Light TapeBlock and discuss what combination of TapeBlocks are required and why.
Learning Outcome: Students will understand what is required to make circuit.
Essential Terms: Light Emitting Diode (LED), Circuit, Power source, Conducitve
Link:
- https://www.tapeblock.com/pages/tutorial/make-a-light-tape-block
- Students may need to make a power TapeBlock depending on the power to be used. https://www.tapeblock.com/pages/tutorial/instruction-cards
Inquiry:
- Does the LED work when it is both directions or only one way.
- Where can you get power from.
Lesson 4: Build a Vibration Circuits
Australian Curriculum Link:
- Science: Sound and vibration (ACSSU020)
- Technology: Investigating digital systems (ACTDIK007)
Hook: Pass around a vibration TapeBlock for student to feel and discuss haptic feedback
Task: Students will create a simple vibration making device using TapeBlocks.
Learning Outcome: Students will understand different types of feedback.
Essential Terms: Vibration, Circuit, Feedback
Link: https://www.tapeblock.com/pages/tutorial/make-a-vibration-tape-block
Inquiry: When and why might vibration motors be used.
Lesson 5: Building a fan.
Australian Curriculum Link:
- Science: Forces and motion (ACSSU076)
- Technology: Creating digital solutions (ACTDIP004)
Hook: Show how fans are used in everyday life
Task: Students will build a small fan using TapeBlocks
Learning Outcome: Understand how to connect a motor to power in a circuit.
Essential Terms: Motor, Fan, Circuit
Link: https://www.tapeblock.com/pages/tutorial/make-a-fan-tapeblock
Inquiry: What happens if you change the direction that the fan is connected to the power.
Introduction to Buttons and Switches
Lesson 6: Creating a Simple Button Switch
Australian Curriculum Link:
- Science: Energy transfer (ACSSU049)
- Technology: Creating digital solutions (ACTDIP004)
Hook: Show how a locking button switch works on a TapeBlock
Task: Students will create a simple switch to control their TapeBlock circuit.
Learning Outcome: Understand how switches control the flow of electricity.
Essential Terms: Switch, Circuit, Control
Link: https://www.tapeblock.com/pages/tutorial/make-a-button-tape-block
Lesson 7: Build a Light Sensor
Australian Curriculum Link:
- Science: Light and its effects (ACSSU080)
- Technology: Using digital systems (ACTDIK007)
Hook: Demonstrate a light sensor in action.
Task: Students will build a light sensor using TapeBlocks
Learning Outcome: Understand how sensors work and their applications.
Essential Terms: Sensor, Light Sensor, Circuit
Link: https://www.tapeblock.com/pages/tutorial/make-light-sensor-tape-block
Lesson 8: Creating a Tilt Switch
Australian Curriculum Link:
- Science: Energy transfer (ACSSU049)
- Technology: Using digital systems (ACTDIK007)
Hook: Show how tilt switches are used in devices like smartphones.
Task: Students will use a tilt switch to control their TapeBlock circuit
Learning Outcome: Understand how tilt switches work and their applications.
Essential Terms: Tilt Switch, Circuit, Control
Link: https://www.tapeblock.com/pages/tutorial/make-a-tape-block-tilt-switch
Electronic Concepts
Lesson 9: Series and Parallel Circuits
Australian Curriculum Link:
- Science: Electrical circuits (ACSSU097)
- Technology: Designing solutions (ACTDEP015)
Hook: Show examples of series and parallel circuits in everyday life.
Task: Students will build both series and parallel circuits using TapeBlocks.
Learning Outcome: Differentiate between series and parallel circuits.
Essential Terms: Series Circuit, Parallel Circuit
Link: https://www.tapeblock.com/pages/tutorial/series-and-parallel-circuits
Lesson 10: Conductors and Insulators
Australian Curriculum Link:
- Science: Properties of materials (ACSSU003)
- Technology: Investigating materials (ACTDEK004)
Hook: Demonstrate a working circuit and ask students to predict what will happen if different materials are used.
Task: Students will test various materials to see if they are conductors or insulators.
Learning Outcome: Identify materials that conduct electricity and those that do not.
Essential Terms: Conductor, Insulator, Circuit
Link: https://www.tapeblock.com/pages/tutorial/tapeblock-conductive-play
TapeBlocks with purpose
Lesson 11: Building Simple Structures
Australian Curriculum Link:
- Mathematics - Shape (ACMMG009)
Hook: Display a simple TapeBlock house and ask students to guess how it was built.
Task: Create a small house using TapeBlocks.
Learning Outcome: Students will develop fine motor skills and understand basic construction principles.
Essential Terms: Structure, shape, building
Link: https://www.tapeblock.com/pages/tutorial/make-a-roof-tapeblock
Lesson 12: Designing a TapeBlock Project
Australian Curriculum Link:
- Science: Applying scientific knowledge (ACSHE083)
- Technology: Designing and evaluating solutions (ACTDEP015)
Hook: Show various TapeBlock projects and their applications.
Task: Students will design and create their own TapeBlock project.
Learning Outcome: Outcome: Apply knowledge of circuits and design to create a functional project.
Essential Terms: Design, Project, Circuit
Link:
TapeBlock Across the Curriculum
- Technical Writing: Have students write detailed project reports, instructions, or user manuals for their electronic projects.
- Presentations: Encourage students to present their projects and findings, enhancing their public speaking and communication skills.
- Storytelling: Build scenes from stories using TapeBlocks to enhance narrative understanding.
- Creative Writing: Use TapeBlocks to create characters or settings that inspire writing projects.
- Measurement: Apply measurement skills when building circuits (e.g., measuring resistance, voltage).
- Geometry: Use TapeBlocks to create different geometric shapes and explore how to make each of them light up.
- Physics: Discuss the principles of electricity and magnetism, such as Ohm's Law and electromagnetic fields.
- Recycling: Use TapeBlocks to create projects that emphasize the importance of recycling and reusing materials.
- Design and Technology: Integrate design thinking into project development, focusing on aesthetics and functionality.
- Visual Arts: Create visually appealing project presentations and circuit designs.
- Sculpture: Use TapeBlocks to create 3D art pieces.
- Interactive Art: Combine TapeBlocks with LEDs and sensors to create interactive installations.
- Safety: Teach the importance of safety when working with electronic components and tools.
- Critical and Creative Thinking: Encourage problem-solving and innovation in project design.
- Ethical Understanding: Discuss the ethical implications of technology use and digital citizenship.
- Intercultural Understanding: Explore how technology impacts different cultures and societies.
- Subjects: Science, Geography, Art, Technology
- Objective: Design and build a model of a town using TapeBlocks and use a robot to navigate the space.
-
Activities:
- Science: Integrate simple circuits to light up buildings or power small motors.
- Geography: Map out the city layout, including green spaces and transportation.
- Art: Decorate the city with creative elements.
- Technology: Use a simple robot to navigate the space and plan different ways to move through the city
- Adaptations: Change the complexity of the layout of the city and if there are moving barriers.
- Subjects: Language Arts, Art, Technology
- Objective: Create a tactile storybook with TapeBlocks that includes light and interactive elements.
-
Activities:
- Language Arts: Write a story and plan the scenes.
- Art: Illustrate the story using TapeBlocks to build scenes.
- Technology: Add LEDs and buttons to make the story interactive.
- Adaptations: Pair students for collaborative work, ensuring each student can contribute according to their abilities.
- Subjects: Mathematics, Technology
- Objective: Design and play math games using TapeBlocks.
-
Activities:
- Mathematics: Create games that involve solving math problems or puzzles.
- Technology: Use TapeBlocks to build game boards and interactive elements.
- Adaptations: Use large, colorful TapeBlocks and provide clear, visual instructions for game rules.
- Subjects: Science, Technology, Art
- Objective: Build and program simple electronic pets using TapeBlocks.
-
Activities:
- Science: Learn about robotics and basic programming.
- Technology: Assemble and program the robotic pets.
- Art: Decorate the pets to give them unique personalities.
- Adaptations: The pet can be animated with technologies including bee-bots, Spheros or microcontrollers
- Subjects: Art, Technology
- Objective: Create an interactive art piece such as a communal mural using TapeBlocks and electronic components.
-
Activities:
- Art: Design and build the art installation.
- Technology: Integrate lights, sensors, and motors to make the art interactive.
- Adaptations: Provide tactile and visual feedback to help students understand how their actions affect the installation.
Creative Use of TapeBlocks
Create a mural using the TapeBlock method where students can add items around a theme. This can enhance critical thinking and teamwork skills.
Use the TapeBlock methods with bubble wrap to make items for a disco or decorations for a party.
Students can create personalized name tags that light up, combining creativity with basic circuitry.
Use TapeBlocks as manipulatives for teaching math concepts like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
Encourage students to use TapeBlocks to build scenes from their favorite stories or books. This can help with comprehension and make reading more interactive and fun.
Use TapeBlocks in art projects to create 3D sculptures, mosaics, or interactive art pieces. Students can explore different shapes, colors, and patterns.
Design obstacle courses or fitness challenges using TapeBlocks. They can be used to mark start and finish lines, create hurdles, or set up stations for different activities.
Integrate TapeBlocks with coding and robotics kits to create programmable projects. Students can build robots or automated systems and learn basic programming skills.
Create simple musical instruments with TapeBlocks, such as drums or xylophones. Students can explore sound, rhythm, and music theory.
Set up problem-solving stations where students use TapeBlocks to create craft items with electronic components such as badges or flower gardens.
Use TapeBlocks to create colorful and dynamic classroom decorations. Students can contribute to decorating the classroom, making it a more inviting and personalized space. For example, create a solar system that is able to light up.
Set up learning stations around the classroom where students can use TapeBlocks to explore different subjects and activities. Rotate the stations regularly to keep things fresh and engaging.
TapeBlock Accessible Practice
Including students with disabilities in learning electronics with TapeBlocks can be highly effective due to their accessible design. Here are some strategies to ensure all students can participate and benefit:
- Supports Hands on Learning: Use clear, step-by-step hands-on instructions to help students understand each part of the project.
- Chunky Blocks: TapeBlocks are designed to be easy to handle, even for students with limited fine motor skills [1].
- Conductive Tape: Using conductive tape simplifies connections, making it easier for students to create circuits without needing precise soldering skills.
- Visibility: The affordances can be seen at a distance.
Adaptable to student’s abilities
- Step-by-Step Tutorials: Provide clear, step-by-step instructions and visual aids to help students understand each part of the project.
- Flexible Pacing: Allow students to work at their own pace, offering additional time and support as needed.
- Peer Support: Pair students with disabilities with peers who can assist and collaborate on projects. This fosters a supportive learning environment.
- Group Projects: Encourage group projects where each student can contribute according to their abilities.
- Quiet Spaces: Create quiet areas where students can work without distractions.
- Sensory Tools: Use alternative output to decrease sensory experiences and to help students stay focused.
- Tinker Time: Allow students to explore and tinker with TapeBlocks freely, encouraging experimentation and discovery.
- Real-World Applications: Relate projects to real-world scenarios that interest the students, making learning more relevant and engaging.
- Celebrate Successes: Acknowledge and celebrate each student's progress and achievements, no matter how small.
- Encouragement: Provide continuous encouragement and positive feedback to build confidence.
By implementing these strategies, you can create an inclusive learning environment where all students can enjoy and benefit from learning electronics with TapeBlocks.
Specific Disability Adaptions
Adapting the course for different disabilities involves adjusting the complexity of the concepts, activities, and the depth of understanding required, it can also require the adjustment of the physical component and language that are used. Here are some suggestions for tailoring TapeBlocks for specific disabilities.
Establish language to orient the block prior to any explanations.

Use the tactile affordance of the componence to enable independent circuit making and success recognition. The vibration motor and fan motors are excellent for this. Use the buzzers with caution, although they are an effect sound cue, they can be annoying in a classroom situation.
Be aware of the non-tactile aspects of the physical components. It is not possible to feel that the wires are covered in plastic so only the end of the wire is conductive. This needs to be explicitly explained.
Cutting small piece of conductive tape while peeling the white backing paper is difficult for blind students. Using small round conductive stickers is a much better solution.
Encourage students to use foam blocks in shades that assist them in making sense of the different types of blocks and their purpose and functional relationships.
Color coding can be used as scaffolding to support the placement of switches in the middle as a yellow block between a red and green block. Using prior knowledge of traffic lights.
The planned sequence of learning is important for people with intellectual disabilities. Providing a completed set of TapeBlocks for exploration and discovery should be provided before attempting to make the TapeBlocks to make the process less abstract.
TapeBlocks provide the opportunity for differential repetition to introduce concepts and repeat them to reinforce understanding. This can be achieved in creative ways by integrating crafting into the activities.
Making button and switch TapeBlocks is quite difficult as the components need to be place in a different configuration to the pattern has been learned. Extra support may be required to minimise frustration.
Use multidirectional components so that success is physically easier.
Have assistants hold the components in the place of adaptive switches or use big switches in the circuits.
Use the appropriate communication tools to provide interactions.
Year Level Adaptions
Adapting the course for different year levels involves adjusting the complexity of the concepts, activities, and the depth of understanding required. Here are some suggestions for tailoring the course to various year levels:
- Simplify Concepts: Focus on basic concepts like identifying electronic components and understanding simple circuits.
- Hands-on Activities: Use more visual and tactile activities, such as building circuits with the large, easy-to-handle TapeBlocks.
- Integration with Play: Incorporate play-based learning, like creating simple experiments with electronic in questions such as how many lights. Alternatively make interactive tactile stories with the TapeBlocks.
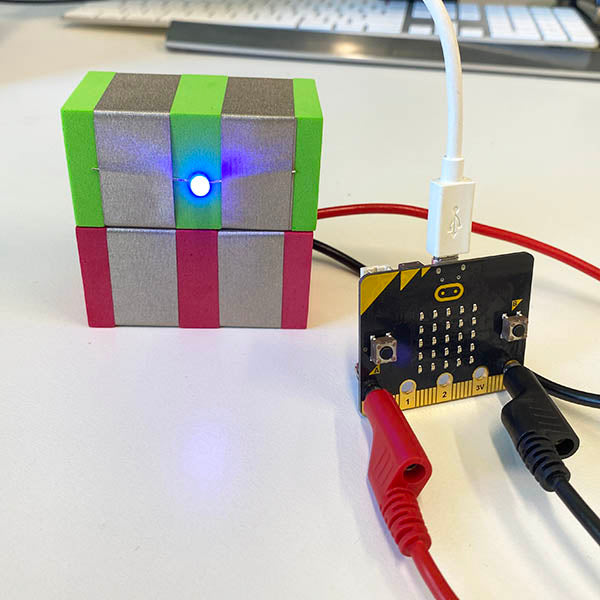
- Introduce Basic Programming: Start with simple block-based programming to control electronic components. This can be done by connecting TapeBlocks to Micro:bits to create simple cause and effect programs.
- Data Representation: Teach basic binary concepts using visual aids and interactive activities.
- Simple Projects: Create small projects, such as a basic light-up card or a simple sensor-based game.
- Intermediate Programming: Move to more complex block-based programming or simple text-based coding.
- Circuit Design: Introduce more components and slightly more complex circuits.
- Problem-Solving Projects: Encourage students to identify problems and design simple solutions using electronics.
- Advanced Programming: Introduce more advanced programming concepts and languages.
- Complex Circuits: Work with microcontrollers and more intricate circuit designs.
- Data Analysis: Teach students how to collect and analyze data from sensors.
- Project Management: Focus on managing larger projects from conception to completion.
- Ethical Considerations: Discuss the ethical and social implications of digital technologies.
- Advanced Digital Solutions: Encourage students to design and implement complex digital solutions to real-world problems.
- Scaffold Learning: Build on prior knowledge and gradually increase the complexity of tasks.
- Differentiate Instruction: Provide various levels of support and challenge based on students' abilities.
- Use Real-World Examples: Relate activities to real-world applications to make learning relevant and engaging.
- Incorporate Feedback: Regularly assess and provide feedback to guide students' learning progress.
Glossary of Terms
Circuit: A complete path through which electricity flows.
LED: Light Emitting Diode, a type of light source.
TapeBlocks: A tool for creating simple circuits using conductive tape and blocks.
Battery: A device that stores and provides electrical energy.
Conductor: A material that allows electricity to flow through it.
Insulator: A material that does not allow electricity to flow through it.
Series Circuit: A circuit where components are connected end-to-end.
Parallel Circuit: A circuit where components are connected across common points.
Switch: A device for making and breaking the connection in an electric circuit.
Sensor: A device that detects and responds to changes in the environment.
Motor: A device that converts electrical energy into mechanical motion.
Tilt Switch: A switch that operates when tilted.
Links
TapeBlocks: A Making Toolkit for People Living with Intellectual Disabilities
Making for all: Encouraging STEM inclusivity for those with ...
Structure | The Australian Curriculum (Version 8.4)
Australian Curriculum - Department of Education
Development of the Australian Curriculum - ACARA
18 Genius Hacks For Your Classroom Using Tape - Bored Teachers
7 smart ways to use technology in classrooms - ideas.ted.com
10 Ways to Use Painters Tape in Your Classroom - Education World
21 Brilliant Binder Clip Hacks All Teachers Need to Try
TapeBlocks make for STEM inclusivity - Education Today
Inclusive STEAM - Monash Assistive Technology and Society
How to build a more inclusive STEM program in early childhood using ...
Relationship of curriculum content to TapeBlocks resources
|
Learning Area or dimension of the curriculum |
Year(s) |
Content description |
Additional comments |
Section of the TapeBlock website related |
Science: Strand: Science understanding – sub-strand: Chemical sciences
|
Year 4 |
AC9S4U04 examine the properties of natural and made materials including fibres, metals, glass, and plastics and consider how these properties influence their use |
Metals / conductive and non-conductive materials including foam and plastics.
Related content with Design and Technologies Years 3 and 4 see below |
TapeBlock: Creative Circuit Making for All describes what TapeBlocks are, and materials needed to create TapeBlock circuits.
|
|
Science: Strand: Science inquiry - Questioning and predicting
|
Year 4 |
AC9S4I01 pose questions to explore observed patterns and relationships and make predictions based on observations.
|
For example, Why do circuits work when assembled in one way but not in a different way?
Related content with Design and Technologies Years 3 and 4 see below |
|
|
Years 3 and 4 |
AC9TDE4K02 describe how forces and the properties of materials affect function in a product or system |
producing models using materials, tools and equipment to show how to control movement, sound or light.
deconstructing a product or system to discover how movement, sound or light can be controlled, for example taking apart a torch or buzzer, or exploring circuit design.investigating the properties of materials to solve problems |
|
|
|
Design and Technologies Strand: Processes and production skills - Investigating and defining |
Years 3 and 4 |
AC9TDE4P01 explore needs or opportunities for designing, and test materials, components, tools, equipment, and processes needed to create designed solutions |
|
· |
|
Science Strand: Science understanding – sub-strand: Physical sciences |
Year 6 |
investigate the transfer and transformation of energy in electrical circuits, including the role of circuit components, insulators, and conductors |
Related content with Technologies: Digital Technologies Year 5 and 6 and Digital technologies Years 5 and 6 (see below) |
TapeBlock: Creative Circuit Making for All describes what TapeBlocks are, and materials needed to create TapeBlock circuits. |
|
Years 5 and 6 |
AC9TDE6K02 explain how electrical energy can be transformed into movement, sound or light in a product or system |
Related content with Year 6 Science: Physical sciences |
|
|
|
Digital Technologies Strand: Knowledge and understanding - Data representation |
Years 5 and 6 |
AC9TDI6K04 explore how data can be represented by off and on states (zeros and ones in binary |
Related content with Year 6 Science: Physical sciences
|
|
|
Years 7 and 8 |
AC9TDE8K03 analyse how force, motion and energy are used to manipulate and control engineered systems |
This is more about the finished products or prototypes that can be made with TapeBlocks such as adding a fan, vibration etc. |
|
|
|
Digital Technologies Strand: Knowledge and understanding – sub-strand: Digital Systems
|
Years 7 and 8 |
AC9TDI8K02 investigate how data is transmitted and secured in wired and wireless networks including the internet |
Circuits and switches are part of the internal components of digital systems |
|
|
Digital Technologies Strand: Knowledge and understanding – sub-strand: Data representation
|
Years 7 and 8 |
AC9TDI8K03 investigate how digital systems represent text, image and audio data using integers |
explaining how circuits can perform binary operations represented as on/off states, for example showing how circuits with 2 switches can represent AND or OR gates |
|
